Combating Mold in Louisiana Schools: Strategies for Prevention and Management to Address Public Health Concerns
Combating Mold in Louisiana Schools: A Public Health Priority
Mold is a common problem in Louisiana schools due to the humid climate and frequent flooding. Mold growth can cause a range of health problems, from allergic reactions to respiratory issues, and can have a significant impact on student and staff well-being. As such, mold remediation in educational facilities is a critical public health priority.
The Prevalence of Mold in Louisiana Schools
According to the Louisiana Department of Health (LDH), mold is a common issue in schools across the state. In response, the LDH has developed guidelines for schools to address mold and other indoor environmental quality issues. However, many schools struggle to implement these guidelines due to a lack of resources or expertise. As a result, mold growth often goes unchecked, putting students and staff at risk.
Health Implications of Mold in Educational Facilities
Exposure to mold can cause a range of health problems, from allergic reactions to respiratory issues. Students and staff who are exposed to mold on a regular basis may experience symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and eye irritation. In severe cases, mold exposure can lead to more serious health problems, such as asthma and other respiratory conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Mold growth is a common problem in Louisiana schools due to the humid climate and frequent flooding.
- Exposure to mold can cause a range of health problems, from allergic reactions to respiratory issues.
- Mold remediation in educational facilities is a critical public health priority.

The Prevalence of Mold in Louisiana Schools
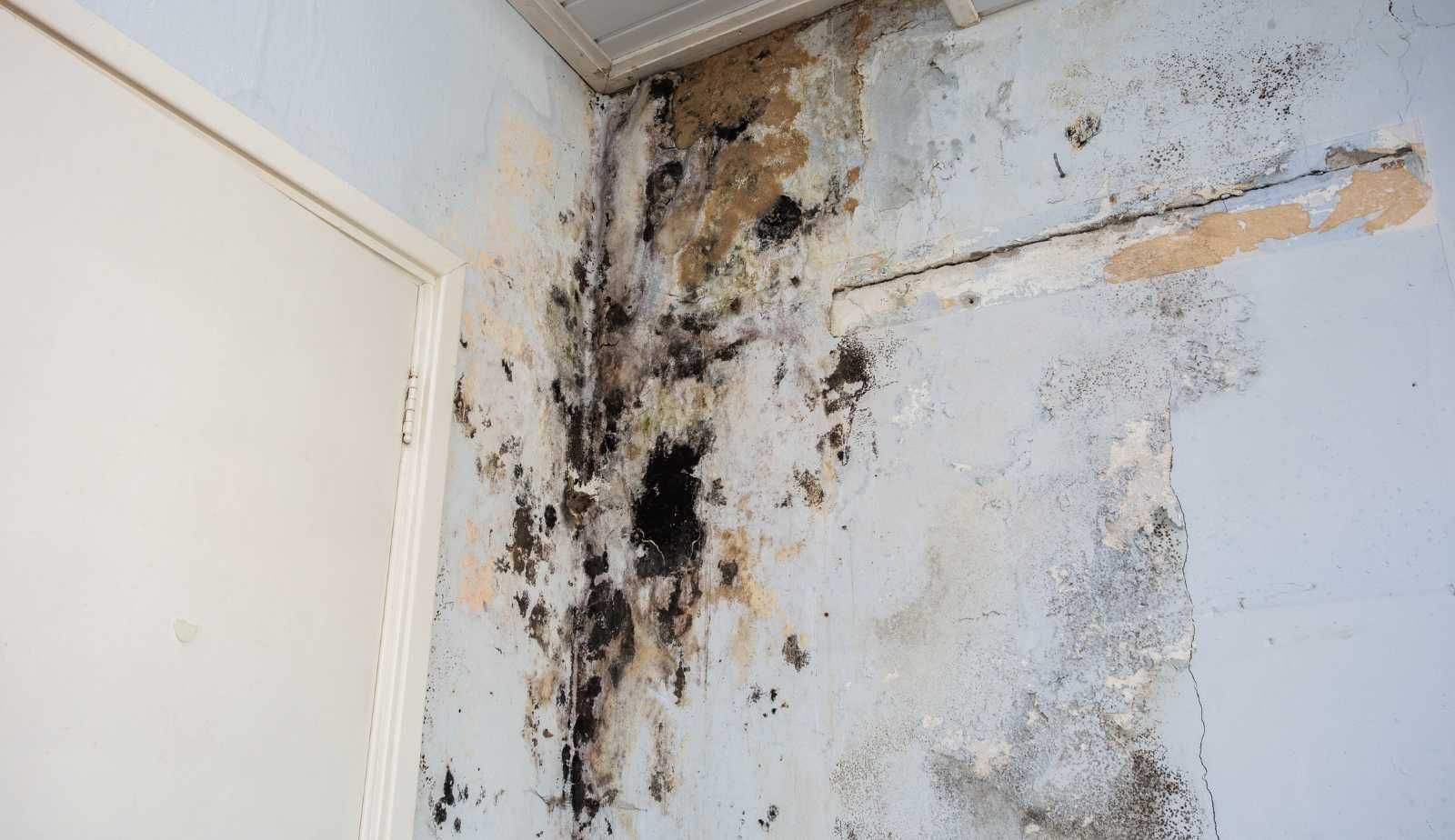
Mold growth in educational facilities is a serious issue that affects the health and well-being of students, teachers, and staff. In Louisiana, where high humidity and frequent hurricanes contribute to moisture problems in buildings, mold growth is a common problem in schools.
Factors Contributing to Mold Growth
Mold requires moisture to grow, and Louisiana's warm and humid climate provides an ideal environment for mold growth. Poor ventilation, water leaks, and flooding can also contribute to moisture problems in school buildings.
According to a report by the Task Force on Mold in Louisiana, "the presence of moisture in buildings is the single most important factor affecting the growth of mold and other fungi." The report also notes that "mold growth can occur on virtually any surface if the moisture problem is not addressed."
Impact of Hurricanes on School Infrastructure
Louisiana is prone to hurricanes and flooding, which can cause significant damage to school buildings and create ideal conditions for mold growth. In the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, many schools in New Orleans were closed due to mold contamination.
According to a study published in the Journal of Environmental Health, "mold growth was found in 46% of the schools in Louisiana that were surveyed after Hurricane Katrina." The study also found that "schools that were flooded during the hurricane had significantly higher levels of mold contamination than schools that were not flooded."
Mold growth in Louisiana schools is a serious public health concern that requires attention and action. Moisture control and mold remediation strategies should be implemented to prevent and manage mold growth in school buildings.
Health Implications of Mold in Educational Facilities
Mold in educational facilities can have short-term and long-term health effects on students, teachers, and staff. The health effects of mold exposure can vary depending on the individual's sensitivity and the amount of exposure.
Short-Term and Long-Term Health Effects
Short-term health effects of mold exposure can include allergic reactions such as sneezing, runny nose, red eyes, and skin rash. In some cases, mold exposure can trigger asthma attacks in individuals with asthma. Long-term exposure to mold can result in more severe health problems such as respiratory infections, chronic bronchitis, and asthma development.
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) found sufficient evidence of an association between mold and other agents in damp indoor environments and upper and lower respiratory tract symptoms, coughing, and wheezing in otherwise healthy people. The IOM also found limited or suggestive evidence linking indoor mold exposure and respiratory illness in otherwise healthy children.
Vulnerable Populations at Risk
Vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, are at a higher risk of adverse health effects from mold exposure. Children spend a significant amount of time in schools, and exposure to mold in these environments can lead to health problems that can affect their academic performance and overall well-being.
It is essential to maintain good indoor air quality in educational facilities to prevent mold growth and minimize the risk of health problems. Strategies for prevention and management of mold include regular inspection and maintenance of HVAC systems, prompt repair of water leaks and moisture problems, proper ventilation, and use of mold-resistant building materials.
Mold in educational facilities can have significant health implications, particularly for vulnerable populations. It is crucial to take proactive measures to prevent and manage mold growth to ensure a safe and healthy learning environment for all students, teachers, and staff.

Regulations and Standards for Mold Remediation
EPA Guidelines and Recommendations
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has developed guidelines and recommendations for mold remediation in indoor environments. These guidelines cover a wide range of topics, including identifying mold, assessing the extent of the problem, and developing a remediation plan. The EPA emphasizes the importance of addressing moisture problems, as mold growth is often a symptom of excess moisture. The guidelines also recommend using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and following proper containment procedures during remediation to prevent the spread of mold spores.
Louisiana Department of Health Policies
The Louisiana Department of Health (LDH) has developed policies and regulations related to mold remediation in educational facilities. These policies outline the responsibilities of school administrators, teachers, and maintenance staff for identifying and addressing mold problems. The LDH also provides guidance on proper remediation procedures, including the use of appropriate cleaning agents and PPE. In addition, the LDH recommends regular inspections and maintenance to prevent moisture problems that can lead to mold growth.
Adherence to these regulations and guidelines is crucial for effective mold remediation in educational facilities. By following these standards, schools can ensure that mold problems are identified and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of health problems for students and staff.
Strategies for Mold Prevention and Management
Mold prevention and management in educational facilities require a multi-faceted approach that involves regular maintenance, effective cleanup and remediation practices, and design and construction considerations.
Maintenance and Regular Inspections
Preventive maintenance is a crucial step in mold prevention. Regular inspections of the building's structure, HVAC systems, and ventilation systems can help identify moisture problems and potential mold growth areas. Moisture problems should be addressed promptly to prevent mold growth.
Effective Cleanup and Remediation Practices
If mold growth is detected, a remediation plan should be implemented immediately. Effective cleanup and remediation practices are essential to prevent the spread of mold and ensure that it is removed safely. The Louisiana Department of Health recommends following the guidelines outlined in the EPA's Mold Remediation in Schools and Commercial Buildings Guide [1] for effective cleanup and remediation practices.
Design and Construction Considerations
Building construction and design considerations play a significant role in mold prevention. Proper building design and construction can help prevent moisture problems that lead to mold growth. Educational facilities should consider using mold-resistant building materials and designing buildings to allow for proper ventilation and moisture control.
Mold prevention and management in educational facilities require a comprehensive approach that involves regular maintenance, effective cleanup and remediation practices, and design and construction considerations. By implementing these strategies, educational facilities can create a safe and healthy environment for students and staff.
The Role of Professional Remediation Services
Mold remediation professionals play a critical role in combating mold in Louisiana schools. They are trained to identify, assess, and remediate mold problems in educational facilities. Engaging professional remediation services is necessary when the mold contamination is extensive, and the affected area is more than ten square feet.
When to Engage Mold Remediation Professionals
Mold remediation professionals should be engaged when mold problems are beyond the scope of in-house maintenance staff. They should also be called in when mold growth is visible, and there is a musty odor. Professional remediation services are also necessary when there is a history of water damage or high humidity levels in the school.
Standards for Professional Judgment and Practices
Mold remediation professionals must adhere to the standards set by the Louisiana State Licensing Board for Contractors. They must also follow the guidelines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). These standards and guidelines ensure that the remediation process is safe and effective.
Mold remediation professionals must wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when performing remediation activities. This equipment includes gloves, goggles, and respirators. They should also use appropriate containment measures to prevent the spread of mold spores to other areas of the school.
In conclusion, mold remediation professionals play a crucial role in combating mold in Louisiana schools. They are trained to identify, assess, and remediate mold problems in educational facilities. Engaging professional remediation services is necessary when the mold contamination is extensive, and the affected area is more than ten square feet. Mold remediation professionals must adhere to the standards set by the Louisiana State Licensing Board for Contractors, the EPA, and OSHA. They must also wear personal protective equipment and use appropriate containment measures to prevent the spread of mold spores to other areas of the school.
Educational Outreach and Resources
Awareness Programs for School Staff and Parents
Educational outreach and awareness programs are essential to inform school staff, parents, and students about the dangers of mold and the importance of mold remediation. Health agencies such as the Louisiana Department of Health (LDH) offer resources and training materials to educate school staff and parents about the health risks associated with mold exposure. The LDH Indoor Environmental Quality Education Service (IEQES) program provides training and resources to school staff and parents to help them identify and prevent mold growth in schools.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also offer resources and training materials to help schools prevent and manage mold growth. The CDC provides information on how to identify and prevent mold growth, as well as guidelines for mold remediation in schools. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also provides guidelines for mold remediation in schools.
Resources List for Further Information
In addition to awareness programs, there are many resources available to help school staff and parents learn more about mold and how to prevent it. Health-care providers can also provide valuable information to parents and students about the health risks associated with mold exposure.
The LDH website offers a comprehensive list of resources for school staff, parents, and students to learn more about mold and how to prevent it. The list includes links to educational materials, guidelines for mold remediation, and information on how to report mold problems in schools.
The CDC also provides a list of resources for schools, including guidelines for mold remediation, educational materials, and links to other resources. The OSHA website provides guidelines for mold remediation in schools and other educational facilities.
By utilizing the educational resources and awareness programs available, school staff, parents, and students can work together to prevent mold growth in schools and ensure the health and safety of everyone in the school community.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the health impacts of mold exposure in educational facilities?
Mold exposure in schools can cause a variety of health problems, including allergic reactions, respiratory issues, and infections. Children, teachers, and staff members who spend time in mold-contaminated environments are at risk of developing health problems. The Louisiana Department of Health warns that mold exposure can cause asthma attacks, irritate the eyes, skin, nose, throat, and lungs of both mold-allergic and non-allergic people. Symptoms other than the allergic and irritant types are not commonly reported as a result of inhaling mold.
What are the EPA guidelines for mold remediation in schools?
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has published guidelines for mold remediation in schools. The guidelines include measures designed to protect the health of building occupants and remediators. The EPA guidelines recommend that schools take immediate action to address water damage and mold growth. The guidelines also provide detailed instructions for identifying and removing mold, as well as for preventing future mold growth.
How does Louisiana law regulate mold remediation in schools?
In Louisiana, mold remediation in schools is regulated by the Louisiana State Licensing Board for Contractors. The board requires that contractors obtain a mold remediation license before performing any mold remediation work. The board also requires that contractors follow specific guidelines for mold remediation, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment and the proper disposal of mold-contaminated materials.
What strategies can schools implement to prevent mold growth?
Schools can implement several strategies to prevent mold growth, including regular inspections, prompt repair of water damage, and proper ventilation. Schools can also reduce indoor humidity levels by using dehumidifiers and air conditioning systems. Additionally, schools can educate staff and students about the importance of reporting water damage and signs of mold growth.
What is involved in obtaining a mold remediation license in Louisiana?
To obtain a mold remediation license in Louisiana, contractors must meet specific education and experience requirements, as well as pass an exam. The Louisiana State Licensing Board for Contractors requires that applicants complete a 16-hour training course on mold remediation and have at least one year of experience in the field. Applicants must also pass a written exam and provide proof of liability insurance.
Why is it essential to have regular mold inspections in schools?
Regular mold inspections are essential in schools to identify and address mold growth before it becomes a health hazard. Mold can grow quickly in damp environments, and it can be difficult to detect without a thorough inspection. Regular inspections can help schools identify and address water damage, leaks, and other issues that can lead to mold growth. By taking proactive measures to prevent mold growth, schools can protect the health of students, teachers, and staff members.




